Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) affects millions, causing breathing to repeatedly stop and start during sleep. Patients now have two primary treatment paths: continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) for instant relief, and tirzepatide (Zepbound), a newer medication that addresses the condition’s underlying causes. While CPAP corrects breathing overnight, tirzepatide supports weight loss and metabolic health, tackling a major driver of OSA.
The Gold Standard: CPAP Therapy
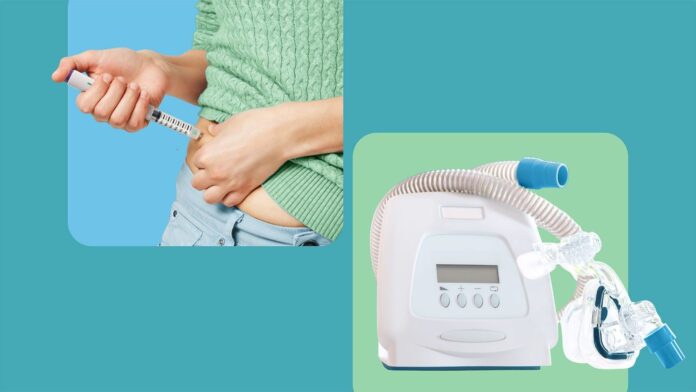
CPAP remains the first-line treatment. The device delivers pressurized air through a mask, keeping airways open. Research confirms its effectiveness: CPAP significantly reduces daytime sleepiness and lowers the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) – the key measure of OSA severity – by up to 31 breathing disruptions per hour. Better sleep leads to improved mood, cognitive function, and reduced risks of heart disease and stroke.
However, CPAP has drawbacks. Some users find the mask uncomfortable or stigmatizing, while others struggle with travel or experience side effects like congestion. Despite these issues, many tolerate CPAP well, experiencing transformative benefits.
The Long-Term Approach: Tirzepatide
Tirzepatide, an FDA-approved injectable medication, is designed for obesity treatment. Excess weight contributes to OSA by depositing fat around the airway. By promoting weight loss, tirzepatide helps improve sleep apnea: studies show it reduces AHI by nearly 22 events per hour. Beyond sleep, the medication offers metabolic benefits like improved blood sugar control and cholesterol levels.
The downside? Tirzepatide takes months to show significant results, unlike CPAP’s immediate effect. It also carries potential side effects, such as nausea, and can be expensive.
Which Treatment is Right for You?
Experts recommend CPAP for most OSA patients. However, those with obesity should also consider tirzepatide, as weight loss can sometimes eliminate the need for CPAP altogether. Some doctors suggest combining both treatments: CPAP for immediate relief while tirzepatide addresses the root cause.
Alternatives exist, including dental devices (for mild cases) and surgically implanted nerve stimulators (for severe, treatment-resistant OSA). ENT surgery is reserved for specific airway obstructions.
Ultimately, the best approach depends on individual factors. Healthy lifestyle changes – regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding alcohol – can complement any treatment plan.
The key takeaway: CPAP offers immediate symptom relief, while tirzepatide provides a long-term solution by tackling obesity. The choice depends on severity, personal preference, and whether weight loss is a viable goal.